Commons:Порог оригинальности
Shortcuts: COM:TO • COM:TOO • COM:THRESHOLD
Порог оригинальности — понятие в авторском праве, которое используется для определения того, может ли определенная работа, или ее часть, быть защищена авторским правом. Оно используется для разграничения одних работ, которые в значительной степени оригинальны и требуют правовой защиты, от тех, которые не требуют. В данном случае «оригинальность» означает «выход из-под пера (оригинального) создателя, автора» (подчеркивая этого автора как правовое лицо), а не «никогда не существовавшее и не встречавшееся до этого» (что могло бы требовать, например, патентной защиты этого нового произведения).
As a rule, copyright applies to a work as a whole. If a work contains a portion that is complex enough to receive copyright protection, then the whole work is considered to be copyrighted. One cannot upload said work to Commons by applying de minimis to the non-trivial portion.
The remainder of this page discusses images judged ineligible for copyright protection by a court or similar authority. It is usually impossible to determine whether a specific image is within the threshold of originality without a judicial decision. However, per precautionary principle, the image should be deleted if there is significant doubt that the image is not copyrighted.
Для дополнительной информации см. Порог оригинальности в Википедии.

Карта
- [This illustration is not explained enough. You may edit the page to make it clearer.]
COM:TOO United States
These images are ![]() OK to upload to Commons, because they are below the threshold of originality required for copyright protection.
OK to upload to Commons, because they are below the threshold of originality required for copyright protection.
-
Bridgeman v Corel 36 F. Supp. 2d 191 (S.D.N.Y. 1999): court ruling that 2D photographs of the original art has no valid claims for new copyrights (case description)
-
NFL abandoned its copyright claims on the fleur-de-lis (news report)
-
Best Western hotels: Consists of letters plus a simple border. None of these is eligible for copyright protection in United States. (authority)
-
DUB magazine: Consists of letters only. None of these is eligible for copyright protection in United States. (authority)
-
Nikken USA Inc. (authority)
-
Bruce Lee core symbol (authority)
-
New York Arrows logo (case report)
-
Car Credit City logo: Copyright office ruled this logo too simple to be protected, but a slightly more complicated version (shown in the linked letter) was accepted for registration (authority)
-
Symbols for "Myst" (authority)
-
Letter S (authority)
-
Registration was cancelled (authority)
-
Registration refused (authority)
-
Ets-Hokin v Skyy Spirits Inc.: Photo is eligible for copyright protection, but not the bottle
-
A plastic version lacked originality (L Batlin & Son v. Snyder)
-
Koosh balls; "inseparable", OddzOn Products, Inc. v. Oman (case report)
-
Map of Arkansas: Addition of shading, colors, labels to a free black and white outline map (case report)
-
Avenue of the Saints logo; registration refused despite compilation copyright claim for arrangement of otherwise unprotectable elements (authority)
-
Geek Squad logo (authority)
-
Subway logo (authority)
-
Discover It logo: the Copyright Office found that the elements, including the shading effect, were insufficiently creative to be copyright-eligible (authority)
-
Cyberpunk 2077 logo (authority)
-
Los Angeles FC logo (authority)
-
Nikon logo (authority)
-
San Francisco Shock logo (authority)
-
Commvault Systems hexagon logo (authority)
-
American Made Logo (authority)
-
Jamba Juice logo (authority)
Despite repeated requests, the US Copyright Office found the Vodafone speechmark (shaded version) ineligible for copyright protection. It cannot, however, be uploaded to Commons because it's a UK logo.
These are ![]() Not OK to upload to Commons (unless published under a free license by the copyright holder), because they are above the threshold of originality required for copyright protection.
Not OK to upload to Commons (unless published under a free license by the copyright holder), because they are above the threshold of originality required for copyright protection.
- These two "no soliciting" signs, although arguably relatively simple, have been issued copyright registration numbers by the United States Copyright Office, which means that they have been reviewed and determined to be eligible for copyright protection. It should be noted that the copyright registration applies to the images as a whole, including their borders.
- A variant of File:CarCreditCity.png with an extra border.
- American Airlines flight symbol VA0002130520; Copyright Office initially refused copyright as being just below the threshold, but upon a higher-resolution submission of the artwork, decided that the shading plus the arrangement pushed the logo just above the threshold and granted a registration. (DR)
- w:File:Disney Junior.svg (VA0001927957).
- w:File:Prince logo.svg (VA0000832222).
- The "Omega Globe Design" (VAu000574660) was assumed to be copyrightable by the Ninth Circuit US Court of Appeals.[1]
- Works from other countries which are above the threshold of originality of the United States but below the threshold of originality of the source country (Hasbro Bradley, Inc. v. Sparkle Toys, Inc.)
- New "pan and scan" versions of films where a widescreen film has been resized to fit the size of a TV screen even if the existing widescreen film is uncopyrighted (Maljack Productions, Inc. v. UAV Corp.)[2]
- In 1951, this mezzotint reproduction of an existing uncopyrighted painting was found to be copyrightable.
- The clothing designs found on pp. 4–5 of the Sixth Circuit's decision in Varsity Brands et al. v. Star Athletica (2015).
- The PAC 12 shield logo en:File:Pac-12 logo.svg (V3617D047).
-
VA0001789579 (and CC-BY 3.0)
- File:Five-element-cycles.jpg ([2]): The arrangement is under a copyright, according to WMF Legal.
- w:File:BP Helios logo.svg is eligible for copyright in the US according to WMF legal, though "not by a lot, but just enough". Note that Commons policy on the country of origin requires this logo to be judged by UK standards. The creativity needed for copyright protection in the UK and most other common law countries is much lower; legal only commented on the threshold of originality in the United States.
- File:REMAX hot air balloon logo.svg: The logo was denied copyright registration as a trivial simplification of an earlier 1998 logo. However, that does not mean that the work as a whole is uncopyrightable; it is still a derivative work of the original logo, and DR consensus was that unlike File:Mickey Mouse head and ears.svg, the derivative still had sufficient creative elements to be copyrightable.
-
VA0001427710 (and Apache License 2.0)
-
VA0001950611 (and Apache License 2.0)
- w:File:PBS logo.svg and w:File:PBS (1984-2019) logo.svg: The PBS logo (VA0001310087). Also see DR1 and DR2
- Juneteenth flag (on English Wikipedia as en:File:Juneteenth flag.webp) (VAu000488555)
- Paintings
![]() Not OK for most paintings.
Not OK for most paintings.
Even seemingly simple paintings consisting of geometric shapes are often copyrighted due to details that may not be immediately obvious to the viewer.
- Photographic reproductions of paintings by Mark Rothko have been granted registration by the US Copyright Office, so it is reasonable to assume that the original works are also copyrighted.
- Red, white and brown (VA0000089094)
- Other
Although the threshold of originality for non-graphic works (such as architecture and sound recordings) follow the same standards, such cases can be difficult to determine.
- The five-note melody that typically accompanies Intel's logo was granted copyright protection because it "combined and blended synthesized, digital sounds" and was "refined and mastered with a special spatial enhancer." [3]
- Anish Kapoor's Cloud Gate is a relatively simple 3D sculpture that was deemed eligible for copyright (VA0001983425)
- The replica of public domain object Statue of Liberty in New York-New York Hotel and Casino is deemed eligible for copyright, also the United States Postal Service is being sued for copyright infringement for famously (and mistakenly) using this statue instead of the real Statue of Liberty on its Forever stamps. (VAu001149387 and VA0001882070) also see (DR1) (DR2)
Civil law countries
Civil law countries usually require a relatively high minimum level of intellectual creativity which will exclude typical signatures and simple logos from copyright protection. However, this does not apply to all such countries. For example, Austria and China are both known to have a relatively low threshold of originality, while a few simple logos from the Philippines gained copyright registrations from the country's Intellectual Property Office.
If you are aware of specific case law or legal advice on this issue in any country, please add a "Threshold of originality" section to the appropriate Commons:Нормы авторского права по странам country subpage, and add a link to it with an entry below.
COM:TOO Afghanistan
Афганистан
According to the 2008 Copyright Law, work that may be protected includes: Photography work that has been created using an innovative mode; Innovative work of handicraft or industrial art (carpet designs, rugs, felt carpet and its attachments etc.); Innovative work which has been created based on the public culture (folklore) or national cultural heritage and art.[2008 Article 6(1) items 7-9]
COM:TOO Austria
Австрия
Austria has a low threshold of originality despite being a civil law country. See the archived discussion on the German Wikipedia.
These logos are ![]() Нет:
Нет:
- Bauer Logo.
COM:TOO Brazil
Бразилия
Примеры:
 Да. В деле Boneco de Preço Miúdo (2011), куклы, которые представляли собой трехмерную и очеловеченную версию логотипа, были сочтены судом недостаточно оригинальными для защиты. Суд счел, что в куклах не было оригинальности или неопубликованной работы, поскольку они представляли уже существующий символ (логотип супермаркета), и что уже существовали предыдущие 3D и гуманизированные версии этого логотипа. Суд не предоставил никакой ценности или правовой защиты конкретной 3D- и гуманизированной версии рассматриваемого логотипа и назвал это чем-то вроде "стилизации, подчиненной предыдущей идее".[9]
Да. В деле Boneco de Preço Miúdo (2011), куклы, которые представляли собой трехмерную и очеловеченную версию логотипа, были сочтены судом недостаточно оригинальными для защиты. Суд счел, что в куклах не было оригинальности или неопубликованной работы, поскольку они представляли уже существующий символ (логотип супермаркета), и что уже существовали предыдущие 3D и гуманизированные версии этого логотипа. Суд не предоставил никакой ценности или правовой защиты конкретной 3D- и гуманизированной версии рассматриваемого логотипа и назвал это чем-то вроде "стилизации, подчиненной предыдущей идее".[9] Да. Авторское право на компиляции / реорганизации уже существующих элементов часто отклонялось в суде, намекая на то, что порог того, что представляет собой "интеллектуальное творение" в этом отношении, в Бразилии довольно высок.[10]
Да. Авторское право на компиляции / реорганизации уже существующих элементов часто отклонялось в суде, намекая на то, что порог того, что представляет собой "интеллектуальное творение" в этом отношении, в Бразилии довольно высок.[10] Да. Лозунги, как правило, приемлемы. В редких случаях они могут быть защищены, когда существует такой уровень творчества, который позволяет достичь уровня литературного произведения. Например, в деле Guerra das Moedas (2013), авторское право на выражение не было признано судом. В вердикте говорилось, что язык является культурным достоянием народа, поэтому языковые выражения не могут быть защищены законом. Дело Rede Globo против Роналдо Чамброни похоже[11][12]
Да. Лозунги, как правило, приемлемы. В редких случаях они могут быть защищены, когда существует такой уровень творчества, который позволяет достичь уровня литературного произведения. Например, в деле Guerra das Moedas (2013), авторское право на выражение не было признано судом. В вердикте говорилось, что язык является культурным достоянием народа, поэтому языковые выражения не могут быть защищены законом. Дело Rede Globo против Роналдо Чамброни похоже[11][12]
Некоторые примеры помогают определить, какие фотографии являются, а какие нет, "художественными произведениями" и, следовательно, объектом защиты в соответствии с законом об авторском праве 1973 года:
 Да. Фасад здания Юнг Фрау в Жоинвилли, а также частичные виды города, сфотографированные очевидным простым способом, без использования какой-либо специальной техники (дифференциада). Суд постановил: "Фотографии не считаются художественными произведениями... которые изображают явно простым способом, без использования какой-либо дифференцированной техники, фасад жилого здания и частичный вид на город, в соответствии с контрактом на обслуживание с бизнесом по недвижимости с заранее определенной рекламной целью".[13]
Да. Фасад здания Юнг Фрау в Жоинвилли, а также частичные виды города, сфотографированные очевидным простым способом, без использования какой-либо специальной техники (дифференциада). Суд постановил: "Фотографии не считаются художественными произведениями... которые изображают явно простым способом, без использования какой-либо дифференцированной техники, фасад жилого здания и частичный вид на город, в соответствии с контрактом на обслуживание с бизнесом по недвижимости с заранее определенной рекламной целью".[13] Да. Простые документальные, описательные фотографии в целом, такие как фотографии, документирующие социальные встречи: В SC-AC 111630 SC 2002.011163-0 (2006): "простая фотографическая документация, не имеющая художественного характера, не подпадает под авторское право... что позволяет использовать копию без упоминания имени фотографа, поскольку, согласно бразильскому законодательству, только художественная фотография (по выбору объекта и условий выполнения) включена в список охраняемых произведений. ... [например] с документальными фотографиями общественных мероприятий, где автор выполнял обязанности ответчика, ссылка на имя фотографа не требуется, поскольку это не художественное произведение..."[14]
Да. Простые документальные, описательные фотографии в целом, такие как фотографии, документирующие социальные встречи: В SC-AC 111630 SC 2002.011163-0 (2006): "простая фотографическая документация, не имеющая художественного характера, не подпадает под авторское право... что позволяет использовать копию без упоминания имени фотографа, поскольку, согласно бразильскому законодательству, только художественная фотография (по выбору объекта и условий выполнения) включена в список охраняемых произведений. ... [например] с документальными фотографиями общественных мероприятий, где автор выполнял обязанности ответчика, ссылка на имя фотографа не требуется, поскольку это не художественное произведение..."[14] Да. В постановлении 2000 года говорилось: "Фотографии для документов, удостоверяющих личность, сделанные автоматическими машинами, не являются художественными произведениями. ... Также не должны быть защищены авторским правом чисто технические фотографии, которые воспроизводят определенный объект без малейшего художественного интереса".[15]
Да. В постановлении 2000 года говорилось: "Фотографии для документов, удостоверяющих личность, сделанные автоматическими машинами, не являются художественными произведениями. ... Также не должны быть защищены авторским правом чисто технические фотографии, которые воспроизводят определенный объект без малейшего художественного интереса".[15] Нет В другом решении 2000 года говорилось: "Фотографии [...] имеют художественный характер, характеризующийся оригинальностью, творчеством и техникой их автора, элементами, которые раскрывают... произведение искусства. Они не являются, как утверждает заявитель, простым воспроизведением изображений в рекламных целях или обычными моментальными снимками".[16]
Нет В другом решении 2000 года говорилось: "Фотографии [...] имеют художественный характер, характеризующийся оригинальностью, творчеством и техникой их автора, элементами, которые раскрывают... произведение искусства. Они не являются, как утверждает заявитель, простым воспроизведением изображений в рекламных целях или обычными моментальными снимками".[16]
![]() Куклы, которые были трехмерной и очеловеченной версией этого логотипа, были сочтены в суде недостаточно оригинальными, чтобы быть защищенными.
Куклы, которые были трехмерной и очеловеченной версией этого логотипа, были сочтены в суде недостаточно оригинальными, чтобы быть защищенными.
COM:TOO Czech Republic
Чехия
The work must be "a unique outcome of the creative activity of the author".[121/2000–2006 Art.2(1)] For photographs and computer programs, it suffices if the work "is original in the sense that it is the author’s own intellectual creation".[121/2000–2006 Art.2(2)]
COM:TOO Chile
Чили
Registration in the Intellectual Property Registry generates a "presumption" of copyright in favor of the registrant. Any work may be registered for "presumed" copyright, but Law No. 17.336 clearly states the "presumed" copyright may be contested. That is because, as established in "Astorga Sánchez José / Inversiones C. S. A.", C-2470-2009, 17.° Juzgado Civil de Santiago (28 October 2011), the Intellectual Property Conservator (Conservador) only makes the deposit of the documents into the registry, does not make an examination of their originality, or to determine whether the deposited documents are works or not, and so certificates of intellectual property generated by the Intellectual Property Registry do not establish that a work is new, original or viceversa. The Conservator of Intellectual Property expressed in 2011 it is up to the judicial system "to carry out an originality test to define whether the creation is indeed a particular manifestation of human ingenuity that can be classified as original compared to other equivalent creations, analyzed from a subjective perspective, that is, that the imprint or trace of the author can be perceived, that allows it to stand out from others". Such pronouncement was adhered to by the 17th civil judge of Santiago.[17]
COM:TOO China
Китай
China has a relatively low threshold of originality standard; basic designs may be copyrightable. One of the most noticeable cases is the logo of a company named Gang Heng (listed below) ruled by China's supreme court as copyrighted (see below).
The following examples are ![]() Да:
Да:
- "Matchstick man" (image) with a black sphere as a head, black lines as torso, limbs and feet is not copyrightable for lacking originality, ruled Higher People's Court of Beijing Municipality (source).
- Five SKECHERS logos (image) are not copyrightable for lacking originality, ruled Higher People's Court of Beijing Municipality in 2020 (final judgement and related news coverage).
- "BIOU" logo (image), with letter "b" and "o", and a small barcode in the upper right corner, is not copyrightable for lacking originality, ruled Higher People's Court of Beijing Municipality in 2018 (final judgement and related articles [3] [4]). Note that the logo was initially ruled as copyrightable by the Trademark Review and Adjudication Board and a lower court.
- "KON" logo (see below), with three black bars crossed together, is not copyrightable for lacking originality, ruled Beijing Dongcheng District People's Court in 2019 (final judgement and news coverage).
- "Chao Qun" logo (see below), is not copyrightable for lacking originality, ruled China's Supreme People's Court in 2012 (original judgment by the Court). The court asserted that the expression does not show the existence of a unique style; there are only subtle differences when compared to the common Seal script and Clerical script, the "Chao Qun" logo does not reach a certain creative height, and does not have originality.
-
A stick figure similar to this image, where the head is represented by a circle and other parts represented by straight lines, is not copyrightable.
-
The SKECHERS's S logo is not copyrightable.
-
KON logo with three black bars crossed together is not copyrightable.
-
Chao Qun logo is not copyrightable.
The following examples are ![]() Not OK:
Not OK:
- Calligraphy works, such as:
- the work "道" on this photo (archived from original) (see the article by Beijing Youth Daily (archived from original), and the follow-up report (archived from original).
- the character "勁" (archived from the original), with rulings made by Beijing No.1 Intermediate People's Court, and Higher People's Court of Beijing Municipality
- calligraphy for "澳門豆撈" (image), ruled by Henan Zhengzhou Intermediate People's Court (source).
- are copyrighted (Copyright Law of the PR China: "Article 2 Works of Chinese citizens, legal entities or other organizations, whether published or not, shall enjoy copyright in accordance with this Law." ; "Article 3 'Works' mentioned in this Law shall include [...] in the following forms: (4) works of fine art and architecture" ; Regulations for the Implementation: "Article 4 (8) 'works of fine arts' means [...] such as paintings, works of calligraphy and sculptures;")
- Handwriting: a hand-written manuscript was deemed copyrightable as work of art, according to a decision made by Nanjing Intermediate People's Court in 2017 (sources: [5] [6], Final judgement).
- "LY" company logo (alternative link; archived from the original), although arguably relatively simple, has been ruled copyrightable by Trademark Appeal Board of the State Administration of Industry & Commerce, Beijing Intellectual Property Court, and Higher People's Court of Beijing Municipality.
- Typefaces of characters "笑", "喜", and "城市宝贝" in these two logos are copyrightable, ruled Nanjing Intermediate People's Court in 2012. However the character "巴" in the same logo was decided not copyrightable for lacking originality in the same decision. (source, court decision full text: Final judgement)
- Gang Heng logo: China's Supreme People's Court ruled this logo to be protected by copyright in 2014 (original judgment by the Court; related news coverage).
- Dyneema logo (in this article): China's Supreme People's Court ruled this logo to be protected by copyright in 2017 (original judgment by the Court).
- K2 Sports logo as shown in the image below is eligible for copyright protection, determined during trademark adjudication proceedings in 2010 (source).
-
The logo of K2 Sports is copyrightable in China (but not copyrightable in its country of origin, the US).
COM:TOO Denmark
Дания
| Status | Example | Notes |
|---|---|---|
 |
Three fonts not eligible for copyright protection (Supreme Court 30 June 2006, U2006.2697H). Two other fonts were found eligible for copyright. | |
 |
Sketches of windows and doors not eligible for copyright protection (The Maritime and Commercial Court 8 August 2003.)[18][19] | |
_01.jpg/100px-WWF_Schweiz%2C_Zürich_Office_(Ank_Kumar%2C_Infosys_Limited)_01.jpg) |
The WWF panda logo is not protected by copyright[20] | |
 |
The GLOBAL knife design is copyright protected in Denmark.[21] | |
 |
A specific chair design (Tripp Trapp).[22] |
COM:TOO Finland
Финляндия
For works of visual art, the threshold of originality is relatively low.[23] Simple logos, however, are generally below the threshold of originality.[24] In particular, the threshold is high when only basic colors and shapes (such as triangles, squares and circles or capital letters) are used.
 |
Simple photograph with limited copyright period – not a photographic work of art. (TN 2003:6) | |
 |
Differences compared to the coat of arms of the historic region did not meet threshold of originality. (TN 1998:5) | |
| Commons:Deletion_requests/Aalto_vases | "The wave-like forms of the [original Aalto vases] do not... result from the intended use of the object but the creative mental effort of the author. [Therefore the original vases] are independent and original enough to be considered works of art as meant in 1 § of [the Finnish Copyright law]" (p. 4). (TN 2010:10) | |
| A specific house type | (Eurohouse S 2, court ruling) | |
| The logo is below the threshold of originality because it is "ordinary and [does] not express an independent and original result of a creative process of its author. Somebody else in undertaking a comparable task could have contrived a similar ... logo". (TN 2000:1) | ||
| Save the Children Fund logo | The logo is above the threshold of originality, because its "visual manifestation is the creative work of its author, whereby the ideological basis of the fund has been successfully conformed with in an independent and original manner... [N]o one else undertaking a comparable task could have reached a similar outcome". (TN 2010:3) | |
and |
The logos are "in their literary and visual manifestation simple and ordinary to the degree that they are not to be regarded as original works in their own regard." (TN 2009:2) | |
| The logo is "is not original and independent in such a way that it would be protected ... by copyright". (TN 2011:7) | ||
| The logo is below the threshold of originality because "its central elements and the way in which they have been combined are commonly used in logos and are thus ordinary". (TN 2000:1) | ||
| "Silmu" logo | Although the logo consists of a "stylized, albeit fairly simple, red tulip", it is above the threshold of originality for works of visual art. (TN 2001:12) |
COM:TOO France
Франция
French law asserts that a work is copyrightable when it bears the "imprint of the personality of the author". In practice, it depends on the work in question, but this has left the bar quite low for many works where an artistic intent can be shown. For an art exhibition, a man placed the word paradis with gold lettering above the bathroom door of the old dormitory of alcoholics at a psychiatric facility, and termed it artwork; the French courts agreed with him that it was copyrightable based on the aesthetic choices made ("affixing the word 'paradise' in gold with patina effect and a special graphics on dilapidated door, the lock-shaped cross, encased in a crumbling wall with peeling paint").
France has "a slightly higher threshold of originality in general, and particularly so in the context of photographic works".
A decision from Supreme court (Cour de Cassation) on October 2011 agreed with appeal court decision saying that a quite artistic picture of two fish on a yellow plate about a traditional Marseille meal could not be protected by French law because of lack of originality.[28] According to this decision, level of originality required by this appeal court is very high. This decision was criticized but French supreme court does not control facts but only controls interpretation of the law.
COM:TOO Germany
Германия
- Works of fine art (including works of applied art and architectural works)
"Works of fine art", as defined in § 2(1)(4) of the 1965 Act on Copyright and Related Rights (Gesetz über Urheberrecht und verwandte Schutzrechte) (UrhG), is a catch-all term for works of fine art in a stricter sense, works of applied art, and architectural works. Fine art is distinguished from applied art by its lack of a utilitarian purpose.[29] For many decades, courts imposed a higher threshold of originality on works of applied art than on works of fine art ("two-tier theory").[30] In 2013, however, the Federal Court of Justice expressly changed its jurisprudence, holding that "in general, the copyright protection of works of applied art is not subject to other requirements than the copyright protection of works of non-utilitarian fine art or of literary or musical creation. It is hence sufficient that they attain a level of creativity that allows a public open to art and relatively familiar with views on art to justifiably speak of 'artistic' creations".[31]
In assessing whether an article with a utilitarian purpose is protected by copyright, one must take into account, however, that the aesthetic effect of the article can only provide a basis for copyright protection to the extent that it is not dictated by the article's utilitarian purpose, but instead is based on an artistic effort.[32] Only those features of a utilitarian article that are not entirely dictated by the technical function can justify copyright protection.[33] A feature is considered "dictated by the technical function" if the article could not function without it.[34] This includes features that, for technical reasons, must necessarily be used in articles of the same kind as the article concerned, as well as features that, while being used for technical reasons, are freely selectable or interchangeable. To the extent that the design of such features is entirely dictated by their technical function, they are incapable of justifying copyright protection of the utilitarian article.[35]
Examples from court cases on applied art:[36]
Protection denied:
- a climbing structure for playgrounds made of ropes (pictured in the decision, p 3 bottom) because the structure consists of freely selectable or interchangeable yet technically required features and does not exhibit artistic creativity;[37]
- a wooden toy train ("birthday train") with wagons in which candles and numbers can be inserted (pictured in the decision, p 3) because there were similar-looking, pre-existing toy trains.[38]
- a logo (pictured here in black and white) consisting of the text "Match by Audiotec Fischer" and the commonly used "fast-forward" symbol because neither the design of the text nor the design of the symbol ("widely used in the audio world") nor the combination of the two could be considered an artistic creation.[39]
Protection accorded:
- a logo consisting of a mouth, eyes, and wave lines ("eyebrows") (pictured in the decision, p 3) (in the case at issue, the design was painted on the exterior of a ship and therefore could be reproduced under the freedom of panorama limitation);[40]
- a toy train comprised of wooden animal figurines on wheels ("birthday caravan") (pictured in the decision, p 3) because it was a complete redesign of pre-existing toy trains, whose locomotive and waggons were replaced with animals, and the overall design (shapes, colours) was not the result of technical necessities but an expression of the author's artistic creativity;[41]
- an urn emblazoned with an airbrushed depiction of a deer (pictured in the decision, on the left);[42]
- a Birkenstock sandal (model "Madrid");[43]
- a Porsche 356 sports car (pictured in the decision, 3rd and 4th image from the top);[44]
- a patio heater with a triangular base (pictured in the decision, first image).[45]
In the past decades, court cases where protection as applied art was eventually accorded primarily revolved around renowned designer objects, in particular items of furniture and lamps.[46] Ещё несколько свежих примеров:
- chairs and tables based on drafts by the designers Marcel Breuer ("Wassily" chair, "Laccio" table) and Ludwig Mies van der Rohe ("Barcelona" chair, stool, couch, and table; "Brno" chair; "Prag" chair);[47]
- the "Wilhelm Wagenfeld table lamp";[48]
- a brilliant-cut diamond ring ("Niessing-Spannring").[49]
COM:TOO Greece
Греция
The term “work” is defined as including any original intellectual creation expressed in any form, including alterations of other works as well as collections of works, provided that the selection or the arrangement of such collections is original.[50]
Originality is understood by Greek jurisprudence as a notion of “statistical uniqueness”, which means that the work involves skill, labor and judgment emanating from the author and that no other person, acting under the same circumstances, could produce the exact same work.[51]
COM:TOO Hungary
Венгрия
![]() Да
Да
- stylized text with a common stylized globe icon (does not show the actual image).
![]() Нет
Нет
COM:TOO Indonesia
Индонезия
COM:TOO Iran
Иран
for most logos. The level of originality required for copyright protection in Iran seems very low.
The following are registrable for copyright protection: "(...) pictures, drawings, designs, decorative writings, (...) or any decorative and imaginative work produced in any simple or complex manner "
COM:TOO Italy
Италия
Hogan Lovells states "In summary, the threshold for an industrial design product to enjoy copyright protection is still quite high and even famous industrial design products have been denied such protection by Italian Courts."
Probably this applies to logos too. These files have been kept as simple logos:
But the logo of AC Parma was deleted as being a complex logo.
COM:TOO Japan
Япония
Logos in the gallery below are ![]() Да to upload.
Article 2 of Japanese copyright law defines that a work is eligible for copyright when it is a production in which thoughts or sentiments are expressed in a creative way and which falls within the literary, scientific, artistic or musical domain.
Да to upload.
Article 2 of Japanese copyright law defines that a work is eligible for copyright when it is a production in which thoughts or sentiments are expressed in a creative way and which falls within the literary, scientific, artistic or musical domain.
Japanese courts have decided that to be copyrightable, a text logo needs to have artistic appearance that is worth artistic appreciation. Logos composed merely of geometric shapes and texts are also not copyrightable in general.

|
(DR) Tokyo High Court's ruling: letters are a means of communication, shared by all. Copyright protection of fonts is limited only to those that raise artistic appreciation as much as artistic works do. [57] |

|
(DR) Tokyo High Court's ruling: although the shape is stylized, the text is in a normal arrangement and keeps its function of being read as a sequence of letters. [58] |

|
Tokyo District Court's ruling: the Court is negative towards recognizing the symbol as a copyrightable work of fine arts, because it is considered merely relatively simple graphic elements. [59] |
- Furby toy: utilitarian, so not protected by copyright as an artistic work. Not utilitarian in the United States, so photos of the toy can't be uploaded to Commons.
COM:TOO Libya
Ливия
COM:TOO Luxembourg
Люксембург
According to Jean-Luc Putz, the threshold of originality in Luxembourg is not as strict as in UK but not as liberal as in Germany. During the legislation the intent was to orientate with other Benelux states or France.
COM:TOO Mexico
Мексика
- Эти изображения
 Да для загрузки на Викисклад
Да для загрузки на Викисклад
-
Буквы, цифры или отдельные цвета
-
Имена и названия или отдельные фразы
-
Простые форматы или пустые формы для заполнения любым типом информации, а также инструкции к ним (пример изображения)
-
Воспроизведение или имитация без разрешения щитов, флагов или эмблем любой страны, штата, муниципалитета или эквивалентного политического подразделения
-
Воспроизведения или имитации без разрешения международных правительственных, неправительственных организаций или любой другой официально признанной организации
- Они
 Нет для загрузки на Викисклад (если только они не опубликованы по свободной лицензии владельцем авторских прав), поскольку они превышают порог оригинальности, необходимый для защиты авторских прав, и не подпадают под действие самого закона.
Нет для загрузки на Викисклад (если только они не опубликованы по свободной лицензии владельцем авторских прав), поскольку они превышают порог оригинальности, необходимый для защиты авторских прав, и не подпадают под действие самого закона.
COM:TOO Netherlands
Нидерланды
Simple logos are okay in the Netherlands but not all logos are. Whether something is above the threshold of originality in the Netherlands is defined in the Supreme Court judgment "'Van Dale/Romme'". In this judgment, the Supreme Court ruled that:[62]
- In assessing the ground of cassation it should be noted that, for a product to be considered a work of literature, science or art as meant in article 1 in conjunction with article 10 of the Copyright law (Auteurswet), it is required that it has an own, original character and bears the personal mark of the maker.
This was further specified in the Supreme Court judgment ''Endstra-tapes':[63]
- The product has to bear an own, original character. In short, this means the shape may not be based on that of another work. (cf. article 13 Aw.) The demand that the product has to bear the personal mark of the maker means that there has to be a shape that is the result of creative human labor and thus creative choices, which therefore is a product of the human mind. In any case, excluded from this is everything that has a shape that is so trivial or banal, that one cannot show any creative labor behind it of any kind whatsoever.
Later the Supreme Court determined in judgment on Stokke v. Fikszo that:[64]
- For a work to be eligible for copyright, it is necessary that the work has an own original character and bears the personal mark of the maker ... The Court of Justice of the European Union has has formulated the benchmark in such a way that it must concern "an intellectual creation of the author of the work".
COM:TOO Norway
Норвегия
- Not protected
Two-minute theatre play.
- Protected
- A specific chair design (Tripp Trapp)
- The logo for the TV series Jul i Blåfjell.
COM:TOO Peru
Перу
Простые фотографии
Старые опубликованные фотографии имеют срок действия авторских прав 20 лет, считая с первого января года, следующего за годом обнародования фотографии до 1976 года. Приведенные примечания основаны на отмененном законе 1961 года:
- Для старых снимков, сделанных до 31 декабря 1975 года и которые не были опубликованы в рамках собственного произведения автора,
 не соответствуют общему определению "произведения" в соответствии с законом 1961 года (и статьей 3.4 Всемирной конвенции об авторском праве: "Положения [...], не применимые к фотографическим произведениям [...], не должны быть менее десяти лет")[68]. Фотография хранилась в течение 20 лет после создания ее первой копии, без представления автором этого в литературном, научном или документальном произведении, начиная с 1 января следующего года.[13714/1961 Art. 27] Они не были продлены в течение даты URAA.[13714/1961 Art. 27 and 57] Используется {{PD-Peru-photo}}.
не соответствуют общему определению "произведения" в соответствии с законом 1961 года (и статьей 3.4 Всемирной конвенции об авторском праве: "Положения [...], не применимые к фотографическим произведениям [...], не должны быть менее десяти лет")[68]. Фотография хранилась в течение 20 лет после создания ее первой копии, без представления автором этого в литературном, научном или документальном произведении, начиная с 1 января следующего года.[13714/1961 Art. 27] Они не были продлены в течение даты URAA.[13714/1961 Art. 27 and 57] Используется {{PD-Peru-photo}}. - Срок действия сокращается в следующих случаях: когда автор не указал название на этикетке с сообщением "Воспроизведение запрещено" или что автор опубликовал произведение без полного имени или под неизвестным псевдонимом[13714/1961 Art. 58]. Срок действия анонимных произведений до 31 декабря 1980 года составлял 15 лет после публикации и истек 1 января 1996 года. Они не были продлены в течение даты URAA. Используется {{PD-Peru-anonymous}}.
- Если они использовались в литературных или научных произведениях, были документальными произведениями или являются репродукциями художественных материалов, "находящихся в частном владении", и автор умер до 1946 года (или до 1966 года, если у кого-то не было наследников в семье), закон рассматривает фотографии как
 авторские работы (в течение жизни и ещё 30/50 лет)[68]. В случае коллективных работ дата считается для последнего остававшегося в живых автора. Если они умерли после 1947 года, они защищены действующим законодательством. Используется {{PD-Peru-1961law}}.
авторские работы (в течение жизни и ещё 30/50 лет)[68]. В случае коллективных работ дата считается для последнего остававшегося в живых автора. Если они умерли после 1947 года, они защищены действующим законодательством. Используется {{PD-Peru-1961law}}.
Срок действия авторских прав на недавно опубликованные фотографии ниже порогового значения составляет 70 лет, считая с первого января года, следующего за годом, когда была сделана фотография. К счастью, этот термин обычно является гибким в случаях и фактах, показанных ниже:
- Общее определение "произведения" в законе 1996 года таково: "любое личное и оригинальное интеллектуальное творение, способное быть раскрыто или воспроизведено в любой форме, которая уже известна или еще может стать известной"[822/1996 Art.2(17)]. Простые фотографии, сделанные или обнародованные с 1976 года, - это те, которые
 не соответствуют общему определению "произведения" и получают только смежные права[822/1996 Art.144], но работы, превышающие этот порог,
не соответствуют общему определению "произведения" и получают только смежные права[822/1996 Art.144], но работы, превышающие этот порог,  получат стандартную охрану (в течение жизни и ещё 70 лет, см. ниже).
получат стандартную охрану (в течение жизни и ещё 70 лет, см. ниже). - Суд Индекопи считает, что оригинальность фотографии должна быть ограничена оригинальностью любой работы, требованиями по защите от плагиата. В соответствии со статьей 3.c Закона о регулировании надписей в реестре Национального закона об авторском праве, предусматривается, что "не могут подлежать регистрации фотографии, которые ограничены простыми воспроизведениями людей, вещей или объектов, уже существующих или демонстрирующих простой документальный характер [...] фотография быть произведением не может представлять собой лишь простое воспроизведение уже существующих объектов"[69].
- Журнал Derecho PUCP рассказывает о примерах отличительных событий, которые превосходят порог оригинальности: творческое использование света, уникальный момент, передача послания в их работе и индивидуальность фотографа. В соответствии с этими и другими критериями простые фотографии подпадают под действие законодательного декрета 1044 о недобросовестной конкуренции[70].
Примеры фотографий в соответствии с законом 1961 года:
-
Фотография в рекламе не считается "литературным произведением". Срок действия защиты изображений истек в 1988 году. Это также не может быть защищено законом 1996 года. См. заявку на восстановление.
-
Фотография сделана в 1973 году для спортивного журнала. Поскольку это журналистское задание для организации, фотография оставалась защищенной в течение 20 лет, до истечения срока ее действия в 1993 году. Это также не может быть защищено законом 1996 года. См. заявку на удаление.
Примеры фотографий в соответствии с законом 1996 года:
- В 2002 году суд счел два изображения бытовой техники ниже порога оригинальности из-за отсутствия творческих доказательств, несмотря на то, что они представлены в каталоге с индивидуальностью. См. решение № 354-2002/TPI-INDECOPI[71].
- Кроме того, в 2002 году суд постановил, что журнальная фотография бойз-бэнда Skándalo в обычной одежде и на однотонном фоне получает смежные права - только потому, что ей не хватает индивидуальности. См. решение № 378-2002/TPI-INDECOPI, Alomi Producciones S.A.C. v Karinto S.A p.13.[69]
- В 2007 году суд признал фотографию подарочной коробки для веб-каталога оригинальной работой из-за выбора оттенка, и в процессе редактирования она содержала тщательные детали, в частности искусственно созданный цветной оттенок. См. решение № 1263-2007/TPI-INDECOPI, Enrique Capella v Grupo Americano de Comercio S.A.C. and Citybank del Perú S.A p.4.[72]
- В 2008 году суд постановил, что моментальным снимкам спортивных, политических или погодных событий в прессе не хватает оригинальности из-за отсутствия предварительной подготовки при их изготовлении. См. решение № 2521-2008/TPI-Indecopi, Agencia Efe S.A. v Las Rosas Editorial S.A.C.
- В 2012 году Суд пришел к выводу, что нехудожественные методы обработки фотографий не подлежат охране (например, сканирование). См. решение № 059-2012/TPI-Indecopi and Indecopi (2015), p.75.[73]
- В 2013 году Indecopi пришел к выводу, что рекламная фотография модели в одежде текстильной компании действительно отличается оригинальностью благодаря обрамлению, фокусу и композиции, подчеркивающей ее наряд. См. решение № 0384-2013/CDA-INDECOPI, Peruvian Connection Ltd. v SENATI p. 9 and 10.[74]
- In 2021 the criteria for originality of photographs were simplified to three points: transmittable, framed and lighting that shows their personality. Between pages 77 and 82 of this resolution the court evident that press photographs from Hildebrandt en sus trece magazine do carry originality because they focus on the gestures of the photographed and the depth of the camera. See Resolution No 0096-2021/TPI-INDECOPI, Plutón Editores S.A.C. v DP Comunicaciones S.A.C..
Видеографический процесс
Для аудиовизуальных произведений существует порог оригинальности, но их защита одинакова как для произведений, так и для записей (публикация/создание + 70 лет). В то время как кинематографические произведения ("obra audiovisual") охраняются в полном объеме, смежные права могут быть предоставлены только производителю нехудожественных съемок ("grabación audiovisual")[822/1996 Art. 140], которые также включают исполнение и радиовещание[822/1996 Art. 143]. Решение 000111-1999-ODA-INDECOPI устанавливает различия между этими двумя терминами, в частности, и аналогично простым фотографиям, фиксирует последовательность изображений. Но, решение 371-2001/TPI-INDECOPI устанавливает, что основным требованием для получения смежных прав от производителя нехудожественных съемок является: "наличие в процессе их создания определенной ![]() степени креативности, технических или организационных навыков достаточной для обоснования признания произведения аналогичное право в их пользу" (например, с оплатой за просмотр событий).
степени креативности, технических или организационных навыков достаточной для обоснования признания произведения аналогичное право в их пользу" (например, с оплатой за просмотр событий).
Теоретически, снимки, сделанные камерой видеонаблюдения в общественном месте, могли бы ![]() из-за отсутствия их производителя (поскольку общественным достоянием в основном считается перуанское государство) оказаться в общественном достоянии. Видеозапись с камер видеонаблюдения Национальной системы Сегуридад Сьюдадана анонимно предоставляется Национальной полиции Перу или прокуратуре, как и с государственных камер в общественных местах, нет никаких известных доказательств от первоначального производителя материала[N° 007-2020-IN Art. 18]. Opinión Consultiva 60-2019-JUS/DGTAIPD указывает, что видеозаписи подлежат разглашению, если они представляют общественный интерес и используются в процессе открытых данных (см. также Работы правительства Перу)[N° 007-2020-IN Art.22], места, снятые на видео, соответствуют "местам общественного достояния"[N° 007-2020-IN Art. 7], мониторинг со стороны человека существует, но не влияет на технические или творческие возможности камеры наблюдения для записи[N° 007-2020-IN Art. 2]. Также это не художественное произведение, поскольку его содержание не может быть изменено по сравнению с оригиналом[N° 007-2020-IN Art. 19], в результате отснятый материал ниже порога оригинальности и не соответствует требованиям статьи 143 закона 1996 года о смежных правах[75][76]. Моральные права лица, задействованного в этом средстве массовой информации, имеют преимущественную силу. Для этих кадров в официальных работах используется {{PD-PE-exempt}}.
из-за отсутствия их производителя (поскольку общественным достоянием в основном считается перуанское государство) оказаться в общественном достоянии. Видеозапись с камер видеонаблюдения Национальной системы Сегуридад Сьюдадана анонимно предоставляется Национальной полиции Перу или прокуратуре, как и с государственных камер в общественных местах, нет никаких известных доказательств от первоначального производителя материала[N° 007-2020-IN Art. 18]. Opinión Consultiva 60-2019-JUS/DGTAIPD указывает, что видеозаписи подлежат разглашению, если они представляют общественный интерес и используются в процессе открытых данных (см. также Работы правительства Перу)[N° 007-2020-IN Art.22], места, снятые на видео, соответствуют "местам общественного достояния"[N° 007-2020-IN Art. 7], мониторинг со стороны человека существует, но не влияет на технические или творческие возможности камеры наблюдения для записи[N° 007-2020-IN Art. 2]. Также это не художественное произведение, поскольку его содержание не может быть изменено по сравнению с оригиналом[N° 007-2020-IN Art. 19], в результате отснятый материал ниже порога оригинальности и не соответствует требованиям статьи 143 закона 1996 года о смежных правах[75][76]. Моральные права лица, задействованного в этом средстве массовой информации, имеют преимущественную силу. Для этих кадров в официальных работах используется {{PD-PE-exempt}}.
Логотипы, дизайны и другие работы
Простые или заурядные логотипы и дизайны ![]() допустимы для загрузки на Викисклад, поскольку они не соответствуют порогу оригинальности, требуемому для защиты авторских прав. Со слов Indecopi и Министерства юстиции и со ссылкой на резолюции № 1349-2001/TPI-INDECOPI (первый абзац) и 0286-1998/TPI-INDECOPI (второй абзац):
допустимы для загрузки на Викисклад, поскольку они не соответствуют порогу оригинальности, требуемому для защиты авторских прав. Со слов Indecopi и Министерства юстиции и со ссылкой на резолюции № 1349-2001/TPI-INDECOPI (первый абзац) и 0286-1998/TPI-INDECOPI (второй абзац):
| “ | Согласно статье 3 Решения 351 [Андского решения], в соответствии со статьей 2 Законодательного декрета №. Согласно статье 822, под произведением понимается любое оригинальное интеллектуальное творение художественного, научного или литературного характера, которое может быть раскрыто или воспроизведено в любой форме. [...] Независимо от того, что уже является частью культурного наследия - художественного, научного или литературного- не будет считаться ни [оригинальным творением], ни [оригинальной] формой выражения, которая вытекает из природы вещей или из механического применения положений определенных правовых норм, ни [оригинальной] формой выражения, которая сводится к простой технике или простым инструкциям, которые только для этого выполнения требуются навыки ручного труда. | ” |
—Indecopi, La originalidad como requisito de protección por derechos de autor ("requisito de la originalidad"), Precedentes y normativa del Indecopi en Propiedad Intelectual (2015)[73] | ||
В 18-м абзаце в Casación Número: 1686-2011 объясняет использование оригинальности в архитектурных произведениях, выполняющих утилитарные функции:
| “ | Оригинальность архитектурного произведения [...] следует искать главным образом в творческих особенностях, которые наиболее отличаются от целей модели, ее природы, географического и ландшафтного контекста и функциональных требований заказчика, а также технических стандартов и стандартов городского планирования, применимых к данному случаю; и скорее, откликаться, определенным образом или в целом, на индивидуальность или художественную индивидуальность автора. [Архитектурная модель] [...] должна быть подвергнута анализу с целью определения того, отвечают ли они только элементам функциональности или природным характеристикам вида, к которому они принадлежат, или, напротив, содержат черты, соответствующие прихоти или индивидуальности, которые автор хотел им приписать., выходящие за рамки их функциональности или технической строгости, что придает изделию индивидуальность по отношению к остальным конструкциям его разновидностей. | ” |
-
Telefónica v Deutsche Telekom (решение № 1127-1998/TPI-INDECOPI)[73]: "Невозможно предоставить монополию на эту букву в пользу одного владельца".
-
Agrotrade S.R.LTDA. v Infutecsa E.I.R.L. (решение № 0286-1998/TPI-INDECOPI)[73]: "Когда очевидно, что творению не хватает индивидуальности и оно было скопировано дословно, это не делает его произведением".
-
решение № 1370-2011/TPI-INDECOPI: "Хотя это не распространенный шрифт и со временем могут проявиться некоторые отличия от классической графики, этого недостаточно, чтобы считать, что работа защищена авторским правом".
-
решение № 0366-2011-TPI-INDECOPI: "Название плаката состоит из предложения без креативности и непосредственно информирует и анонсирует содержание мероприятия".
-
Corporación Oro Verde S.A.C. v Industrias Alimenticias Cusco S.A. (решение № 008-2008/CDA-INDECOPI): "Границы с мотивами инков и шрифт, используемый для обозначения слова "КУСКО", не отвечают требованиям оригинальности, достаточным для того, чтобы считаться художественным произведением".
-
Carga Máxima v Del Barrio and Compañía Peruana de Radiodifusión (решение № 0209-2019/CDA-INDECOPI): суд определил, что "скрипучий стиль шрифта" с плакатов Чичи для этого логотипа не является оригинальным из-за его распространенного использования.
-
Решение № 0546-2005/TPI-INDECOPI: На "рисунке" они несут тексты и корону Статуи Свободы, которым не хватает индивидуальности.
-
Решение № 0698-2014/TPI-INDECOPI: "Тот факт, что [...] восклицательный знак написан неправильной формой и что каждая буква или знак имеет разный цвет, [не] определяет, что такие характеристики наделяют дизайн, поданный на регистрацию, признаками оригинальности, требуемыми нормой для обеспечения его охраны как произведения".
-
Решение № 1194-2017/TPI-INDECOPI: "Суд отмечает, что в нем отсутствуют оригинальные элементы, поскольку это рисунки, не представляющие какой-либо особенности, которые были воспроизведены обычным способом, без включения какого-либо элемента".
-
Решение № 1192-2017/TPI-INDECOPI (см. решение № 1194-2017/TPI-INDECOPI).
-
Решение № 4301-2015/TPI-INDECOPI: "Это декоративные элементы, которым не хватает оригинальности, поскольку одни и те же или похожие на них используются разными людьми и компаниями для идентификации".
-
Empresas Luc-Chetti S.A. v Molinoitalia S.A. y Pragma DePublicidad S.A. (решение № 074-2000/TPI-INDECOPI): "[...] хотя музыкальные произведения содержат мелодию, гармонию и ритм, исключительные права на мелодию могут быть приобретены только".[77]
-
Решение № 211-94-DA-INDECOPI: "защита [...] не распространяется на алфавитную сортировку пользователей, содержащуюся в [телефонной книге]"
-
Решение № 2418-2009/TPI-INDECOPI: Хотя угол наклона ручки к горизонтальной линии или глубина вогнутой части чайной ложки [немного отличается] от стандартной формы [...] объект не является оригинальной работой из-за обычной формы других чайных ложек.[79]
-
Решение № 0184-2008/TPI-INDECOPI: Миниатюрное изображение Мачу-Пикчу из пластика не может быть выдано в качестве оригинальной работы, поскольку его регистрация запретила бы людям создавать другие миниатюрные версии цитадели.[79]
-
Решение № 1645-2007/TPI-INDECOPI: "Разработка [портативной сцены] (подобной этому изображению), возможно, потребовала интеллектуальных усилий со стороны ее создателя, но у нее недостаточно характеристик, чтобы считаться произведением [3D] искусства, поскольку она состоит из простого расположения съемных панелей в виде экрана".
-
Решение № 0148-2008/TPI-INDECOPI: "Однако Суд считает, что предоставление охраны дизайну, состоящему исключительно из фигур или рисунков, находящихся в общественном достоянии, такому как Инка чакана, означало бы, что ни одно другое лицо не сможет использовать такие рисунки, принадлежащие к общему культурному наследию".
-
Решение № 0083-2011/DDA-INDECOPI не предусматривает защиту от использования Tumi с общим текстом.
-
Новостная лента, на которую не распространяется защита авторским правом, но изображение, также не считающееся авторским произведением, подлежит соответствующей охране в течение 70 лет после создания.
-
Resolución N° 0082-2023/TPI-INDECOPI: "The additional elements that appear on the images (e.g. rectangles containing phrases or expressions) also do not present particular features that denote a minimum of originality, so they cannot be protected by copyright"
Примечание: Некоторые творения превышают порог оригинальности и ![]() недопустимы для загрузки на Викисклад:
недопустимы для загрузки на Викисклад:
- Логотип Tres Olivas: лист с тремя оливками, отличающийся тональностью, использованием яркости и ощущением движения. См. решение № 1774-2012/TPI-INDECOPI, Olivos del Sur S.A.C. vs Antonio Moncayo Cortés[80].
- Эмблема La Primera. См. решение № 2361-2016/TPI-INDECOPI.
- Вымышленный персонаж в фильме "Супермен": "Крис из криптонита Кримсона". См. решение № 1164-2014/TPI-INDECOPI.
- Логотип с изображением людей с факелом рядом с буквой E, над буквой T. "Triunfo Empresarial". См. решение № 0319-2018/TPI-INDECOPI.
COM:TOO Philippines
Филиппины
COM:TOO Poland
Польша
Per Tomasz Targosz (Institute of Intellectual Property Law, Jagiellonian University Kraków):
[81]Polish copyright law has quite a long tradition of setting the threshold rather low, which may encourage frivolous lawsuits forcing courts to ponder whether simple graphic designs, short lines of text or even names should or should not be protected by copyright law.
COM:TOO Portugal
Португалия
w:File:Juventude Socialista Portugal.png was deleted as it was considered to be above the threshold of originality.
- Photographs
In Portugal photographs have been consistently specifically required to have a significant degree of creativity in order to be copyrighted. Article §164 of the current 2017 copyright law states that "the choice of a photograph's subject and the conditions of its creation must be deemed to be a personal artistic creation by the author before a photograph may qualify for protection".
- Court cases
- Landscape photograph: Ruled as without originality. In 2009 the Tribunal da Relação de Lisboa ruled as void of copyright for lack of artistic creativity a landscape photograph the author was claiming copyright on due to his choice of the setting, light and other conditions. It was considered by the court "a vulgar photograph resultant from the mere choice of an object, such as a city council building and part of a group of trees, without a minimum of creativity".[82] The subject is discussed in a 2017 article published by the Instituto Portugues de Fotografia.
- Heart reproduction commissioned to a laboratory in order to be presented in an exposition: Ruled as without originality.[82]
- Clothing/Fashion: Ruled as without originality.
- Puppets wearing Madeira national costumes (generally tourist souvenirs) following old and common models were considered without copyright.[85]
COM:TOO Russia
Россия
- Произведения, созданные автоматической камерой
![]() используется {{PD-RU-exempt-autocam}}
используется {{PD-RU-exempt-autocam}}
![]() Да Фотографии и видеоролики, сделанные автоматической (но не автоматизированной) камерой, не являются субъектом авторского права, так как созданы техническим средством без творческого вклада человека. П. 80 постановления Пленума Верховного суда Российской Федерации № 10 от 23 апреля 2019 года.
Да Фотографии и видеоролики, сделанные автоматической (но не автоматизированной) камерой, не являются субъектом авторского права, так как созданы техническим средством без творческого вклада человека. П. 80 постановления Пленума Верховного суда Российской Федерации № 10 от 23 апреля 2019 года.
Примеры
- Любая фоторабота или видеосъемка, сделанные с помощью автоматической камеры для записи административных правонарушений (например, с помощью автоматической камеры для фиксации нарушений Правил дорожного движения[86]). Пункт 80 постановления Пленума Верховного Суда Российской Федерации от 23 апреля 2019 г. № 10.
- Простые творческие работы
![]() Нет Простой результат творчества (творческой деятельности человека) защищен авторским правом. П. 80 постановления Пленума Верховного суда Российской Федерации № 10 от 23 апреля 2019 года.
Нет Простой результат творчества (творческой деятельности человека) защищен авторским правом. П. 80 постановления Пленума Верховного суда Российской Федерации № 10 от 23 апреля 2019 года.
Пример
- Чёрный квадрат как геометрическая фигура сам по себе не защищен авторским правом. В то же время «Чёрный квардрат» Казимира Малевича защищен авторским правом, потому что эта картина является результатом творческой работы в общепризнанном художественном стиле «супрематизм» и находится в общественном достоянии из-за истечения срока защиты авторского права, а не из-за простоты результата.
- Логотипы
![]() Под вопросом В российских судах нет явного прецедента порога оригинальности для простых логотипов.
Под вопросом В российских судах нет явного прецедента порога оригинальности для простых логотипов.
COM:TOO Senegal
Сенегал
COM:TOO Slovenia
Словения
The threshold of originality in Slovenia depends on the field of creativity. If the maneuvering space of the possible creativity is narrower, it requires more creativity for a work to be copyrighted.
In this regard, the following court cases are relevant:
Applied arts:
- VSL0069492 - the design of a couch set has been found to be below the threshold.
- VS0011606 – the design of a sales stand has been found to be above the threshold.
Architecture:
- VSL00432 – only the works that constitute an original artwork are copyrighted; the renovation plan of Ljubljana Castle as well as the newly built and (at least some of) the renovated parts of the castle count as such.
Logo:
- VSL00013281 – the logo with inscription "I Feel Slovenia" [7] was found to constitute a copyrighted work.
- The court opined: "The slogan and the logo, which contains both verbal and graphic elements, do not allow them to be separated. Only the synergy of the verbal and graphic elements allows the observer to identify the overall message of the author's work."
Titles:
- VS07924 – the title "Brez zavor" (meaning "Without inhibitions") has been found to be below the threshold.
COM:TOO South Korea
Республика Корея
According to a machine translation of the Copyright Act as amended up to Act No. 14634 of March 21, 2017,
- "Work" refers to a creation that expresses human thoughts or feelings.[432/1957–2017 Article 2.2]
The Supreme Court of South Korea declared that it is sufficient to be work if:[88]
- it is not just an imitation,
- it has own characteristics as a product of mental efforts, and
- it can be distinguished from existing ones.
Seoul High Court judged the seagull pattern and the figure of Ebisu of EVISU Japan is not copyrighted because they cannot be recognized for originality.[89] Also, The Supreme Court of South Korea has ruled that typefaces are not copyrighted. (See also Commons:Copyright rules by territory/South Korea § Signatures)
However, the Supreme Court of South Korea judged the logo of Fox Racing is copyrighted.[90]
COM:TOO Spain
Испания
STS 4443/2004 notes that a work must have the characteristics of "uniqueness, individuality and distinguishability" to qualify for protection.[91]
STS 1644/2017 concerns architecture and states "The terms in which an architectural project is drawn up largely respond to the technical or functional requirements and compliance with urban regulations. When this is the case, the project or the architectural buildings are not protected by copyright in the part imposed by those technical, functional or normative requirements"; and more generally, "the factor of recognizability or differentiation of the work with respect to the pre-existing ones [is] essential to grant an exclusive right with moral and patrimonial aspects".[92]
COM:TOO Sweden
Швеция
"A simple general rule is that if it is unlikely that two persons would create, for example, a text identically or similarly, the text is probably sufficiently original to qualify as a protected work. (..) Often, the requirements for copyright protection are considered to be relatively low."
| Status | Пример | Notes |
|---|---|---|
 |
The text itself can't be considered to fulfill the general threshold of originality considered for copyright protection. This same interpretation is made whether one sees it as Roman numerals or Latin letters. The logo itself does have some figurative design. The font must however, despite some inconsistancies along the edges, be considered as ordinary and the black rectangle in the background does not contribute to any distinctive character. - Patent- och registreringsverket (Swedish Intellectual Property Office) Invändningsärende nr 2017/00120/01, Registrering nr 540495 | |
 |
The logo consists of an a and a 6. The round part of each character is not closed, however the characters are, besides that, made in a fairly ordinary font without any distinctive character. Between the characters is a simple, sun-feather resembelling, figure with a pointy tip which goes down between the characters. Above this figure there are four points, two to the left and two to the right. The logo is way to simple to be granted such copyright protection which can constitute an impediment for others' trademark registration. - Patent- och registreringsverket (Swedish Intellectual Property Office) Invändningsärende nr 2005/0006/0001, Registrering nr 369154.
This ruling was appealed to Patentbesvärsrätten (Patent court of appeals) which settled the original ruling (Mål nr 06-304, vm.reg. 369.154), albeit with one member of the court with a dissenting opinion. Unfortunately, they did not elaborate as to why they settled the original ruling. | |
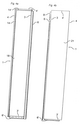 |
Technical drawing. According to decision by the Swedish Supreme Court.NJA 2004 s. 149 | |
| https://shop.textalk.se/shop/4541/files/entombed/ENT_logo_web.png | The logo has been created using a Gothic font in a way which is frequently used among bands in the genre in question [death metal]. The logotype can thus not be considered to fulfill the demands of originality and distinctive character needed for copyright protection. - Patent- och registreringsverket (Swedish Intellectual Property Office) Invändningsärende 2013/0133/0001, Registrering nr 514059.
According to the court, after a comprehensive assessment, the wordmark shows such level of indivudual, distinctive character that it must be considered to possess copyright protection. The court especially values the font of choice, the individual design of the first and last letter and the fact that the first and last letter has been written in caps. - Patent- och marknadsdomstolen (Patent and Market Court) PMÄ 10796-16 This ruling was appealed to Patent- och marknadsöverdomstolen (Patent and Market Court of Appeals) which settled the previous ruling (Mål nr PMÖÄ 5441-17). Unfortunately, they did not elaborate as to why they settled the previous ruling. | |
| A black-and-white version of fr:File:Dunderklumpen Logo.png | Ruled above the TOO by Patent- och registreringsverket (Swedish Intellectual Property Office) (Varumärkesansökan nr 2014/00870), another part of the same ruling was appealed to the Patent- och marknadsdomstolen (Patent and Market Court) which settled the original ruling (Mål nr PMÄ 10748-16). Neither instance elaborated further as why the logo was ruled above the TOO but one can speculate that it was because it was a very obvious case. | |
| Michelin man lamp | Ruled above the TOO by Patent- och registreringsverket (Swedish Intellectual Property Office) (Varumärkesansökan nr 2015/03538). The office did not elaborate further as why the logo was ruled above the TOO but one can speculate that it was because it was a very obvious case. | |
 |
Mini Maglite torch (Mål: T 1421-07, Högsta domstolen) | |
| Porcelain [8] | "Sundborn", made by Rörstrand | |
| Photo illustrating a newspaper article | RH 2009:18 (removed from the website in 2004 because of copyright infringement, protected as a photographic work for 70 years after author's death) | |
| Knitted tunic | (NJA 1995 s. 164) | |
| Technical drawings | (NJA 1998 s. 563) |
COM:TOO Switzerland
Швейцария
Swiss copyright law defines works as "literary and artistic intellectual creations with individual character, irrespective of their value or purpose".[94] Such works are protected by copyright: "Up to 70 years after the death of the author (50 years for computer programs); 50 years from the taking of a photograph without individual character; 70 years from the performance/publication of a phonogram or audio-visual fixation; 50 years from the transmission of a broadcast."[95] This section discusses some types of subject matter.
Photographs: Photographs may be protected as works on the basis of their individual character (individual photographs). Some photographs that lack individual character may also enjoy protection (non-individual photographs).
- Individual photographs: The individual character may manifest itself in a variety of ways, such as the choice of the depicted object, the decision on when the picture is taken, or the editing work done after the picture has been taken.[96] In a 2003 decision, the Federal Supreme Court of Switzerland held that a photo of Bob Marley taken at a concert by a spectator with a handheld camera was eligible for protection as a photographic work because it had the required individual character by virtue of the aesthetic appeal of the picture, combined with the orientation of the picture's components and the distribution of light and shadow. It also found that the photograph was a "creation of the mind" by being shot at a specific time during the singer's movement on the stage.[97] By contrast, in the 2004 case Blau Guggenheim v. British Broadcasting Corporation, the Court found that a photo (en:File:Christoph Meili 1997-nonfree.jpg), shot by a reporter to document Christoph Meili with the files he had taken from his employer, lacked individual character. It found that the scope of conceptual and technical possibilities was not exploited, and that the photograph did not distinguish itself in any way from what was common use.[98] The copyright in an individual photograph lasts for 70 years from the end of the calendar year in which the author died.[99]
- Non-individual photographs: Effective 1 April 2020, Swiss law also protects certain non-individual photographs. Article 2(3bis) URG provides that "photographic depictions and depictions of three-dimensional objects produced by a process similar to that of photography are considered works, even if they do not have individual character". While no individuality is required, according to the official motives accompanying the (eventually adopted) revision draft, these photographs are still required to be "based on human actions", and thus "automatically created photographs such as radar pictures, pictures from surveillance cameras or camera traps" are ineligible for protection.[100] It should be noted that the new right also applies to photographs created before 1 April 2020 that had previously not been protected for failing the individuality test; however, if a particular use of a non-individual photograph was "begun prior to the commencement" of the new law, it "may be completed".[101] According to the official motives, this has the effect that "if non-individual photographs are used on a web page, the web page may be maintained after the entry into force of the protection of non-individual photographs. If, on the other hand, such photographs are included into an existing or a new web page after the entry into force of this protection, permission is required from the owner of the rights in the non-individual photographs."[102] The copyright in a non-individual photograph lasts for 50 years from the end of the calendar year in which the photo was taken.[103]
COM:TOO Taiwan
Китайская Республика (Тайвань)
The level required for copyright is low. Independently created works with "minimal creativity" are eligible, according to Taiwan's Intellectual Property Office.
The following examples are ![]() Да:
Да:
- These two artworks with traditional design elements are unprotected, according to court decisions that they do not meet the originality threshold for copyright protection:
- Simple typeface, such as the typeface of Sunshow company logo:
The following examples are ![]() Нет:
Нет:
- Calligraphy works, including:
- "燒烤飯糰" on this photo, is copyright protected ruled by a court.
- "風月堂" (see the last page of the PDF document for the work in question).[108]
- The graphic part of Sunshow company's logo. The court ruled that the graphic part of the logo: two hands clasped together, one over the other, is copyrightable, but the typeface "SUNSHOW" is not.[109]
- The Louis Vuitton Monogram Multicolor pattern [9][110].
COM:TOO Turkey
Турция
Common law countries
Common law countries typically use a "skill and labour" test to determine the minimum level of originality capable of attracting copyright protection. The required level is extremely low in some countries such as Australia and the United Kingdom. However, Canada and India are major two exceptions. Without some research into individual laws, it cannot be assumed that a text logo from a Common law country is necessarily allowed on Commons. If there is real doubt about the position a local court would take, then the image must be deleted under the precautionary principle.
If the logo is extremely simple (e.g. in a standard font), it will not be eligible for copyright even in Common law countries.
If you are aware of specific case law or legal advice on this issue in any country, please add a "Threshold of originality" section to the appropriate Commons:Copyright rules by territory country subpage, and add a link to it with an entry below.
COM:TOO Australia
Австралия
COM:TOO Canada
Канада
Стандарт креативности подразумевает, что что-то должно быть новым или неочевидным — понятия, более уместно связанные с патентным правом, чем с законом об авторском праве. И по этим причинам я прихожу к выводу, что “оригинальное” произведение в соответствии с Законом об авторском праве - это произведение, созданное автором и не скопированное с другого произведения. Однако одного этого недостаточно, чтобы обнаружить, что что-то является оригинальным. Кроме того, оригинальная работа должна быть результатом мастерства и суждения автора. Применение навыков и суждений, необходимых для создания работы, не должно быть настолько тривиальным, чтобы его можно было охарактеризовать как чисто механическое упражнение".
В том же деле также говорилось:
Чтобы произведение было “оригинальным” по смыслу Закона об авторском праве, оно должно быть чем-то большим, чем просто копией другого произведения. В то же время он не обязательно должен быть творческим в смысле новизны или уникальности. Что требуется для обеспечения защиты авторских прав при выражении идеи, так это проявление мастерства и суждения. Под мастерством я подразумеваю использование своих знаний, развитых способностей или практических способностей при создании работы. Под суждением я подразумеваю использование своей способности к различению или способности формировать мнение или оценку путем сравнения различных возможных вариантов создания работы. Это упражнение в мастерстве и суждении обязательно потребует интеллектуальных усилий.
COM:TOO Hong Kong
Гонконг
![]() Нет for most logos. The level of originality required for copyright protection is presumably very low.
Нет for most logos. The level of originality required for copyright protection is presumably very low.
Because Hong Kong was a territory of the United Kingdom until 1997, Hong Kong law is modeled on UK law, and in the absence of any specific case law to the contrary it is reasonable to assume that the rules will be similar. See the United Kingdom for more details.
COM:TOO India
Индия
India seems to have a similar threshold of originality as the US Courts, called Modicum of Creativity. Older cases may have similar thresholds of originality to the UK Courts called Sweat of the brow but this is no longer applied. Robbin Singh has written an essay on the subject that may be useful.
COM:TOO Ireland
Ирландия
![]() Unknown
Unknown
Despite uncertainty on the required level of originality needed to qualify for copyright protection, images that have been retained on Commons include:

|
ISPCA official logo | Commons:Deletion requests/File:ISPCA official logo.png |
COM:TOO Israel
Израиль
Although Israel historically used a "skill and labour" test similar to that used by the UK, since the 1989 Israeli Supreme Court's ruling in Interlego A/S v. Exin-Lines Bros. SA they have tended fairly close to a US-style requirement equating originality with human creativity.[112] In Israel, the Supreme Court in the Interlego A/S v. Exin-Lines Bros. SA decision adopted the Feist ruling with regards to both the interpretation of the originality requirement and the general rejection of the ‘sweat of the brow’ doctrine and the labour theory as a legitimate interest for establishing a copyright claim.
COM:TOO Malaysia
Малайзия
The threshold of originality situation in Malaysia remains ![]() Unsure. Some previous discussions:
Unsure. Some previous discussions:
- The File:Hcc.png was deleted probably based on calligraphic Chinese words, and cited that COM:TOO UK may also applied for deletion;
- But the File:Petronas Logo.svg was nominated and decided to keep twice, despite that this may also beyond COM:TOO UK. Note that this logo is used before June 2013, and since that, the Petronas modified their logo to be more modern and fairly complex, the current Petronas logo is located at English Wikipedia for Fair use, though some users oppose that.
COM:TOO Nigeria
Нигерия
COM:TOO New Zealand
Новая Зеландия
As stated in the New Zealand government's NZGOAL copyright guide (January 2015),
- As the Court of Appeal has stated, the “threshold test for originality is not high”, the determining factor being “whether sufficient time, skill, labour, or judgment has been expended in producing the work”. The Court has also reiterated the axiom, or principle, that copyright is not concerned with the originality of ideas but with the form of their expression. A work is not original, however, if (a) it is, or to the extent that it is, a copy of another work; or (b) it infringes the copyright in, or to the extent that it infringes the copyright in, another work.
COM:TOO Singapore
Сингапур
COM:TOO United Kingdom
Великобритания
![]() Да for Lego bricks (see w:Interlego v Tyco Industries).
Да for Lego bricks (see w:Interlego v Tyco Industries).
![]() Нет for most logos. The level of originality required for copyright protection in the United Kingdom is very low.
Нет for most logos. The level of originality required for copyright protection in the United Kingdom is very low.
In determining whether a work is protected, typographical copyright, publication rights and database rights need to be considered.
These images are eligible for copyright protection:
- en:File:EDGE magazine (logo).svg (uploaded as free in the US only on en.wikipedia.org): British courts have ruled it eligible for copyright protection,[114] with the judge finding:
[The defendants] submitted that the claimant can have no copyright in its EDGE logo because it is not original over the Franklin Gothic typeface. I do not accept this submission. The stretching of the font was combined with the distinctive slash and projection on the middle bar of the "E". What is required for artistic originality is the expenditure of more than negligible or trivial effort or relevant skill in the creation of the work: see Copinger and Skone James on Copyright 16th Ed at 3-130 and Ladbroke v. William Hill [1964] 1 WLR 273 at 287. The claimant's logo is original within this test.
— Mrs Justice Proudman, in: Future Publishing Ltd v The Edge Interactive Media Inc & Ors [2011] EWHC 1489 (Ch) at [10][115]
Digital copies of images
In 2014 (updated 2015) the UK's Intellectual Property Office issued an advice notice, which said, in part:
Error: No text given for quotation (or equals sign used in the actual argument to an unnamed parameter)
Under section 6 of the European Union (Withdrawal) Act 2018, this decision remains generally binding on UK courts.
This was restated in a November 2023 Appeal Court judgement (THJ v Sheridan, 2023) which confirmed that no new copyright is created in making a photographic reproduction of a two-dimensional public domain artwork, and that this has been the case since 2009.[117][118]
Логотипы и флаги
- The logos in these images may *not* be eligible for copyright protection
-
claimed not to reach the threshold
-
(DR)
-
(DR) "PD text logo -- no question"
-
(Australian company logo DR) "PD-textlogo"
-
(Canada company logo DR) "PD-textlogo"
-
(DR)
-
(DR)
-
(DR)
-
(DR)
- File:Hercules 1998 Intertitle.png originally "background isn't elaborate or eligible for any type of copyright" (decided here in 2010), deleted in 2012 as "shows artistry beyond the TOO".
Архитектура
Images which have been kept because of lack of originality or de minimis:
Note that some of these decisions were controversial.
Фотографии
Photographs which have been deemed ineligible for copyright protection:
-
(DR) Photograph of a three-dimensional object (drawer pull) with bevels and cast shadows
Карты
Maps which have been deemed ineligible for copyright protection:

Darden v. Peters: the addition of "font and color selection; visual effects such as relief, shadowing, and shading; labeling; call-outs" and anti-aliasing to a preexisting map is below the threshold of originality
Use: {{PD-map}}. See the section farther down on partial copying or cropping of uncopyrightable elements from copyrighted works.
See also:
- Commons:Map resources and its sections on public domain maps on the web.
- Open.Michigan Wiki. Casebook archive on "whether or not the content object is protected by US Copyright law.". Opening in the maps section. Data-driven maps in particular are in the public domain. The map represents data. All choices made in the creation of the map being based upon utilitarian and informational considerations. See also: Commons talk:Threshold of originality#Casebook. More locations. See this University of Michigan Casebook archive here. It loads much faster than the Casebook at archive.org.
- Public domain maps. From: Public Domain Sherpa. A copyright and trademark lawyer.
- Category:PD map
Диаграммы
Charts which have been deemed ineligible for copyright protection. Use: {{PD-chart}}. See the section farther down on partial copying or cropping of uncopyrightable elements from copyrighted works. See also:
- Commons:Chart and graph resources and its section on public domain charts on the web.
- Open.Michigan Wiki. Casebook archive on "whether or not the content object is protected by US Copyright law.". Opening in the charts section. See also: Commons talk:Threshold of originality#Casebook. More locations. See this University of Michigan Casebook archive here. It loads much faster than the Casebook at archive.org.
- Category:PD chart
-
See discussion.
-
See the info in the author section of the file description.
-
See the deletion discussion, and this discussion.
-
See the deletion discussion.
-
See the deletion discussion.
Partial copying or cropping of copyrighted works
When a file copies only part of a copyrighted work, that file's copyright status is determined only by what it has copied. If it only copied uncopyrightable elements, then the file is also uncopyrightable. In other words, we judge the copyright status of a file only by what the file itself contains, not by the status of other content the original source contained that was not copied by the file.
 |
This image of the front cover of a novel is public domain in the USA because it only copies uncopyrightable text, not copyrightable contents of the book itself or possibly-copyrightable contents of the back cover. (DR) It would probably not be PD in UK because of the UK's publisher's 25 year copyright on typography, except for the fact that this typographical arrangement was published over 25 years ago. |
Lower threshold in United Kingdom etc.
- File:BBC.svg and many associated variants for BBC divisions were kept, because they only contain Gill Sans, which is an old, standard font.
See Commons:Deletion requests/File:BBC.svg. - File:Clerical Medical.png (uploaded as non-free content (fair use) on en.wikipedia.org)
See Commons:Deletion requests/File:Clerical Medical.png (with reasoning of the EDGE logo).
Смотрите также
- {{Licensed-TOO}} template for formatting and internationalization of licenses of TOO images
- Викисклад:Правила авторского права попредметно
- Category:Threshold of originality related deletion requests
- Commons:When to use the PD-scan tag/ru - on the level of originality needed for a scan of a work to generate a copyright independent of the work
- Commons:Когда использовать тег PD-Art - on the level of originality needed for a photo of a work to generate a copyright independent of the work
- meta:Wikilegal/Copyright threshold of originality for logos
- Category: PD-ineligible license tags
- Category: PD ineligible
- Commons:Chart and graph resources. Including other public domain resources.
- Commons:Map resources. Including other public domain resources.
Примечания
| Some citation text may not have been transcluded |
|---|
|
For more complete, working references see Commons:Нормы авторского права по странам and the individual countries and territories:



















.svg/120px-Subway_logo_(with_slogan).svg.png)









_Nettivihje_logo.gif/80px-Pelastakaa_Lapset_(Save_the_Children_Fund)_Nettivihje_logo.gif)

.gif/80px-K-Plussa_logo_(old).gif)



.svg/87px-Inter_Old_Logo_(2007-2014).svg.png)




.png/86px-Inca_Kola_Advertisement_Hartog_Bell_(cropped).png)

![Telefónica v Deutsche Telekom (решение № 1127-1998/TPI-INDECOPI)[73]: "Невозможно предоставить монополию на эту букву в пользу одного владельца".](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/ad/Telefonica_1984.png/120px-Telefonica_1984.png)
![Agrotrade S.R.LTDA. v Infutecsa E.I.R.L. (решение № 0286-1998/TPI-INDECOPI)[73]: "Когда очевидно, что творению не хватает индивидуальности и оно было скопировано дословно, это не делает его произведением".](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d3/Label_VECCYPER_in_Resolución_Nº_0286-1998%2C_Indecopi.png/97px-Label_VECCYPER_in_Resolución_Nº_0286-1998%2C_Indecopi.png)



![Empresas Luc-Chetti S.A. v Molinoitalia S.A. y Pragma DePublicidad S.A. (решение № 074-2000/TPI-INDECOPI): "[...] хотя музыкальные произведения содержат мелодию, гармонию и ритм, исключительные права на мелодию могут быть приобретены только".[77]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/e/e2/5as_e_8as_diretas_permitidas_nas_partes_intermediárias_-_quinta_em_parte_extrema.png/120px-5as_e_8as_diretas_permitidas_nas_partes_intermediárias_-_quinta_em_parte_extrema.png)
![Решение № 211-94-DA-INDECOPI: "защита [...] не распространяется на алфавитную сортировку пользователей, содержащуюся в [телефонной книге]"](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/86/Annuaire.jpg/120px-Annuaire.jpg)
![Далекий от фантастики, Дафф - это элемент, который по отдельности не имеет защиты произведения искусства. Впоследствии Fox удалось получить идентификационные характеристики для регистрации в качестве торговой марки пива (решение № 1508-2009/TPI-INDECOPI).[78]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/2/21/The_Simpsons_Duff_Beer.jpg/120px-The_Simpsons_Duff_Beer.jpg)
![Решение № 2418-2009/TPI-INDECOPI: Хотя угол наклона ручки к горизонтальной линии или глубина вогнутой части чайной ложки [немного отличается] от стандартной формы [...] объект не является оригинальной работой из-за обычной формы других чайных ложек.[79]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/f/f0/Cucharadita_de_té_(in_Resolution_2418-2009).png/107px-Cucharadita_de_té_(in_Resolution_2418-2009).png)
![Решение № 0184-2008/TPI-INDECOPI: Миниатюрное изображение Мачу-Пикчу из пластика не может быть выдано в качестве оригинальной работы, поскольку его регистрация запретила бы людям создавать другие миниатюрные версии цитадели.[79]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/e/eb/Machu_Picchu%2C_Peru.jpg/120px-Machu_Picchu%2C_Peru.jpg)
![Решение № 1645-2007/TPI-INDECOPI: "Разработка [портативной сцены] (подобной этому изображению), возможно, потребовала интеллектуальных усилий со стороны ее создателя, но у нее недостаточно характеристик, чтобы считаться произведением [3D] искусства, поскольку она состоит из простого расположения съемных панелей в виде экрана".](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/db/Screen_(PSF).png/120px-Screen_(PSF).png)










.svg/120px-Logo_of_the_LG_Corporation_(1995-2014).svg.png)












